Acids, Bases and Salts
Acids, Bases and Salts: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Acids and Bases, Lewis Acids, Conjugate Bases, Conjugate Acids, Bronsted-Lowry Acids, Conjugate Acid-base Pairs, Arrhenius Acids, Limitations of Bronsted-Lowry Theory, Arrhenius Bases and, Bronsted-Lowry Bases
Important Questions on Acids, Bases and Salts
Difference between Lowry theory and Lewis theory
Amongst the given options which of the following molecules/ion acts as a Lewis acid?
The volume of aqueous required to neutralize of aqueous is (Assume complete neutralization)
Which statement about the following equilibrium is true?
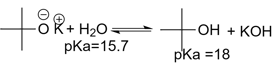
The complete set of Lewis acids among the given compounds is
All Bronsted bases are also Lewis bases, but all Bronsted acids are not Lewis acids. Explain.
What is the difference between acid and salt.
A mixture containing and inert matter weights 0.75gm. When the aqueous solution is titrated with, the colour of phenolphthalein disappears when 21.00 ml of the acid has been added. Methyl range is then added and 7.00 ml more of the acid is required to give red colour to the solution. The % of is...
A mixture containing and inert matter weights 0.75gm. When the aqueous solution is titrated with, the colour of phenolphthalein disappears when 21.00 ml of the acid has been added. Methyl range is then added and 7.00 ml more of the acid is required to give red colour to the solution. The % of is... (Report the answer in the nearest integer value)
Is is a Lewis acid or Lewis base?
can act as a weak acid as well as a weak base. Explain.
What are the limitations of Bronsted Lowry theory?
Explain giving example, Arrhenius acid-base theory. Mention the limitations of this theory.
According to Lewis concept which one of the following is not a base?
Define bases according to Lewis theory.
Which is a better Lewis acid or ?
